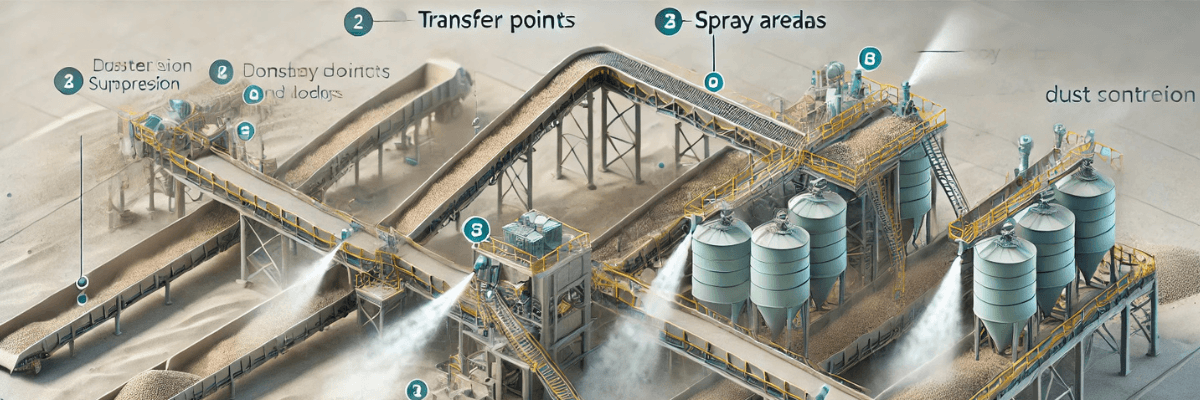
Effective Placement and Positioning of Dust Suppression Nozzles: a Practical Guide
Dust suppression systems are a crucial part of pollution control in industries like mining, manufacturing, and construction. While choosing the right suppression technology is important, the effectiveness of these systems largely depends on the placement and positioning of the nozzles.
In this guide, we’ll explore practical strategies for optimizing nozzle placement to achieve maximum dust suppression, reduce operational costs, and enhance workplace safety.
Why Nozzle Placement Matters
The placement and positioning of dust suppression nozzles determine:
- Coverage: Ensuring the mist or spray reaches the dust-prone areas.
- Efficiency: Minimizing water or chemical waste while maximizing dust control.
- System Longevity: Preventing wear and tear by avoiding exposure to high-velocity dust streams or material impact.
Improper nozzle placement can result in:
- Ineffective dust suppression.
- Wetting of materials, causing clogging and operational issues.
- Increased water or chemical consumption.
Factors to Consider for Nozzle Placement
- Dust Source Location
- Identify areas where dust is generated, such as transfer points, crushers, and loading zones.
- Focus suppression efforts at these hotspots to capture dust at its origin.
- Material Properties
- Consider the type of material being handled (e.g., hydrophobic or moisture-sensitive).
- Adapt the nozzle type and positioning to suit the material’s characteristics.
- Airflow Dynamics
- Account for airflow patterns around the dust source.
- Place nozzles in positions where they can counteract turbulence and capture dust effectively.
- System Accessibility
- Ensure nozzles are easy to access for cleaning, maintenance, and adjustment.
- Use quick-release covers or flexible connections for convenient servicing.
Best Practices for Nozzle Placement
1. Position Nozzles at the Beginning of Transfer Points
At conveyor transfer points, place nozzles near the entry to ensure dust suppression starts as material begins to drop. This allows the moving material to fold the suppressant into the dust stream effectively.
2. Avoid Direct Impingement on Surfaces
Direct spray onto surfaces can cause material buildup and excessive water consumption. Position nozzles to:
- Create a mist or fog above the dust source.
- Allow airborne particles to collide with water droplets naturally.
3. Maintain Proper Distance from the Dust Source
Position nozzles at an optimal distance to ensure adequate coverage without over-saturating the area. This distance depends on:
- The nozzle’s spray pattern and flow rate.
- The size of the area to be treated.
4. Use Shrouding for Enclosed Systems
For enclosed conveyor belts or chutes, position nozzles within shrouds to:
- Minimize mist dissipation due to wind or turbulence.
- Maximize the time dust particles remain in contact with the mist.
5. Angle Nozzles Appropriately
Adjust nozzle angles to ensure even distribution of the mist. Common practices include:
- Angling nozzles at 45° for conveyor belts.
- Positioning nozzles horizontally for vertical drops.
Placement Scenarios for Dust Suppression Nozzles
1. Conveyor Belts
- Use nozzles along the belt’s skirted areas to confine dust within the material body.
- Ensure the cover is 1 meter above the material and the shrouded length is three times the belt speed (in meters per second).
2. Crushers
- Position nozzles above the crusher inlet and near the discharge point.
- Use a combination of mist and foam systems to tackle high dust volumes effectively.
3. Loading Zones
- Install nozzles to create a water curtain around the loading area.
- Ensure coverage on all sides to prevent dust from escaping.
4. Stockpiles
- Use rain guns or fog cannons for large stockpiles.
- Place nozzles at elevated positions to achieve wide-area coverage.
Common Nozzle Types and Their Applications
| Nozzle Type | Best For | Features |
| Cone Spray Nozzles | General material handling | Creates a cone-shaped spray pattern. |
| Flat Fan Nozzles | Belt cleaning or wetting edges | Provides a thin, even spray. |
| Ultrasonic Fog Nozzles | Moisture-sensitive materials | Generates ultra-fine droplets (<10µ). |
| High-Pressure Mist Nozzles | Dust control in open areas | Produces fine mist with wide coverage. |
Maintenance and Monitoring for Optimal Performance
- Regular Cleaning
- Remove dust or material buildup on nozzles to maintain spray quality.
- Use filtered water to prevent clogging.
- Periodic Adjustment
- Check nozzle alignment to ensure consistent coverage.
- Adjust spray angles based on changing operational conditions.
- Replace Worn Nozzles
- Monitor for signs of wear, such as uneven spray patterns or reduced droplet size.
- Replace nozzles as needed to ensure effective dust suppression.